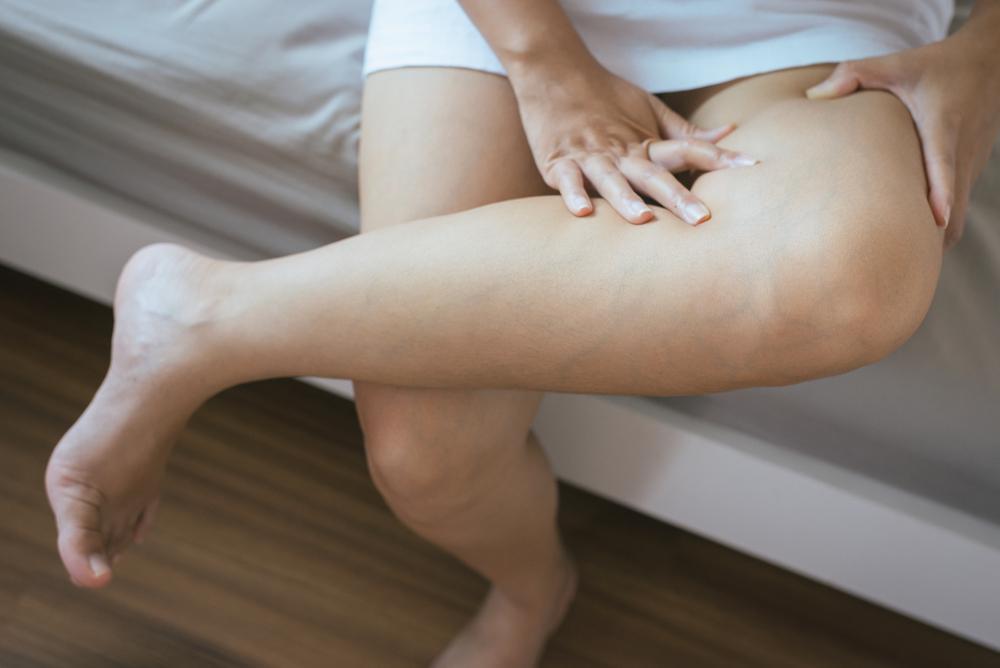
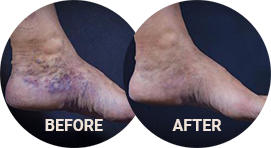
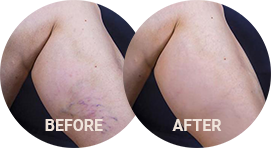
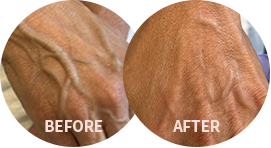
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a disorder that usually affects one leg, when a blood clot forms and blocks blood flow. If the clot breaks up and travels to your lungs, a DVT has the potential to cause a life-threatening pulmonary embolism.
Some medical conditions can affect the way your blood clots, and periods of inactivity can also contribute to DVT. Understanding your risk for developing the condition, recognizing its symptoms, and knowing when to get emergency treatment may all contribute to saving your life.
Contents
Risk Factors for Developing a DVT
Anything that prevents the normal circulation of blood in the deep veins of your legs could cause a DVT. This includes injuries, surgery, medications, or periods of restricted motion such as bed rest or long-distance flights. There are specific factors that increase your risk of developing a DVT. These include:
- Family history of blood clotting disorders, pulmonary embolism, or DVT
- Pregnancy, alone or in combination with other factors
- Medications that affect hormone levels, such as hormone replacement therapy or birth control pills
- Tobacco use
- Heart failure
- Obesity
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Age
- Venous insufficiency
- Certain types of cancer and some cancer treatments
- Venous outflow impairment (Iliac vein compression in the pelvis)
DVT Symptoms
It’s possible for you to have a DVT without any signs or symptoms. Generally, it affects one side, but it’s not impossible to experience a DVT on both sides simultaneously. Swelling is the most common symptom of DVT. This may be accompanied by pain, usually starting in your calf. You may feel sore, or like your muscles are cramping. Your leg may feel warm, and it may appear discolored, typically red.
Signs of Pulmonary Embolism
If you develop a pulmonary embolism as a complication of DVT, you’ll need emergency medical attention as soon as possible because your life could be in danger. Symptoms of pulmonary embolism include:
- Discomfort or pain in your chest that intensifies as you breathe deeply or cough
- Fainting, dizziness, or lightheadedness
- Increased heart rate
- Shortness of breath that comes on suddenly
- Blood appearing when you cough
If you have reason to suspect you might have a DVT, contact Premier Vein Clinic and Dr. Naar’s team will schedule you as soon as possible.
Treating a DVT
Once DVT is diagnosed, blood thinners are typically the first treatment. While these decrease your blood’s ability to clot, they won’t break up existing clots. They’ll prevent existing clots from getting bigger, however. These drugs may be administered by injection, intravenously, or with oral medications.
Thrombolytics, also called clot busters, may be used if you have severe clots. Since they can cause heavy bleeding, their use is usually restricted for the most serious cases of DVT. When other therapies aren’t suitable, a filter may be placed in a large vein, called the vena cava, to prevent clots from reaching your lungs.
Treating DVT promptly reduces the potential for a life-threatening embolism. If you have DVT risk factors, don’t wait for symptoms to show up, because in some cases a pulmonary embolism may be your first warning.
Dr, David Naar is one of the pioneers in the treatment of DVT, iliac vein compression and venous outflow impairment. These conditions are associated with leg pain and swelling. If you suffer from leg swelling, pain or visible veins, call his office for an appointment. It could save your life!
Contact Dr. Naar at Premier Vein Clinic for a thorough DVT assessment. Through treatment and lifestyle changes, you can reduce your chances of developing a DVT. Call the clinic in Westlake, Ohio, or click the button to make an appointment today.